
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
- Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):307-314. Published online March 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0386

- 5,465 View
- 247 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The national healthcare systems of every country in the world cannot sustain the rise in healthcare expenditure caused by chronic diseases and their complications. To sustain the national healthcare system, a novel system should be developed to improve the quality of care and minimize healthcare costs. For 20 years, our team developed patient-communicating digital healthcare platforms and proved their efficacy. National scale randomized control trials are underway to systematically measure the efficacy and economic benefits of this digital health care system. Precision medicine aims to maximize effectiveness of disease management by considering individual variability. Digital health technologies enable precision medicine at a reasonable cost that was not available before. The government launched the “National Integrated Bio-big Data Project” which will collect diverse health data from the participants. Individuals will share their health information to physicians or researchers at their will by gateway named “My-Healthway.’ Taken together, now we stand in front of the evolution of medical care, so-called “Precision medicine.” led by various kinds of technologies and a huge amount of health information exchange. We should lead these new trends as pioneers, not as followers, to establish and implement the best care for our patients that can help them to withstand their devastating diseases.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,987 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
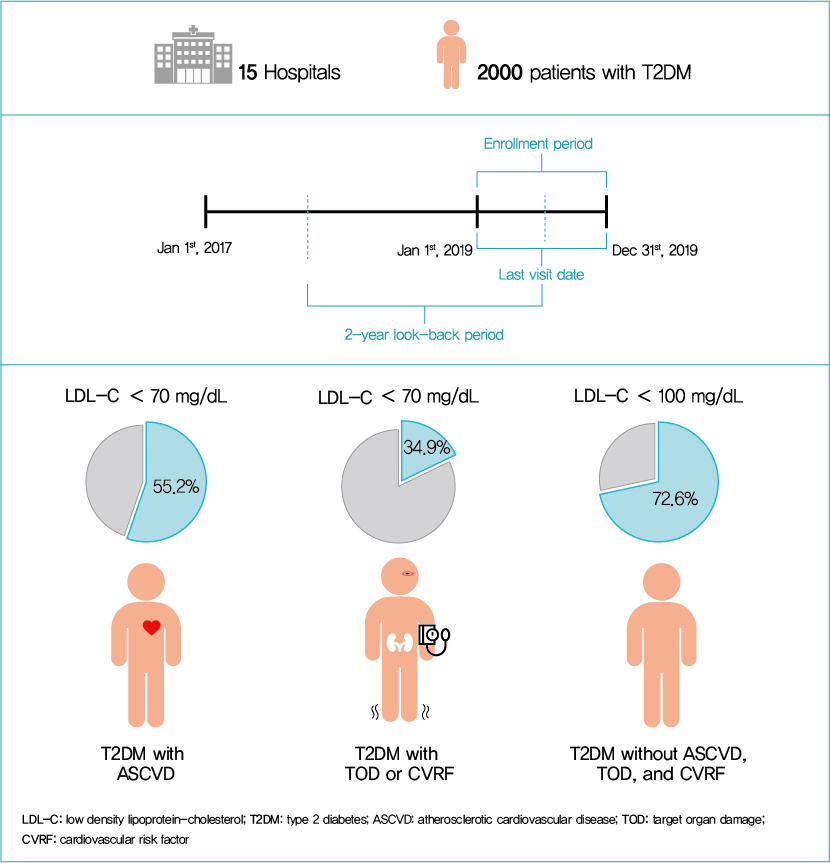
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Complications
- Risk Factors for the Development and Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
- Kyung-Jin Yun, Hye Ji Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Hyun Baek, Young Jung Roh, Ki-Ho Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):473-481. Published online September 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.473
- 4,421 View
- 44 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Some patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) do not develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD) despite the presence of advanced diabetic retinopathy (DR). We aimed to investigate the presence of DKD and its risk factors in patients with T2DM and advanced DR.
Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study in 317 patients with T2DM and advanced DR. The phenotypes of DKD were divided into three groups according to the urine albumin/creatinine ratio (uACR, mg/g) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2): no DKD (uACR <30 and eGFR ≥60), non-severe DKD (uACR ≥30 or eGFR <60), and severe DKD (uACR ≥30 and eGFR <60). Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure, mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, and HbA1c variability (standard deviation [SD] of serial HbA1c values or HbA1c-SD) were calculated for the preceding 2 years.
Results The prevalence of no DKD, non-severe DKD, and severe DKD was 37.2% (
n =118), 37.0% (n =117), and 25.8% (n =82), respectively. HbA1c-SD and the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio correlated positively with uACR and negatively with eGFR. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that the HbA1c-SD and TG/HDL-C ratio were significantly related with eGFR. Multiple logistic regression analyses after adjusting for several risk factors showed that HbA1c-SD and the TG/HDL-C ratio were significant risk factors for severe DKD.Conclusion The prevalence of DKD was about 60% in patients with T2DM and advanced DR. HbA1c variability and TG/HDL-C ratio may affect the development and progression of DKD in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
Charles C. Wykoff, Diana V. Do, Roger A. Goldberg, Dilsher S. Dhoot, Jennifer I. Lim, Weiming Du, Fabiana Q. Silva, Rutvi Desai, Hadi Moini, Kimberly Reed, Alyson J. Berliner, Robert Vitti, W. Lloyd Clark
Ophthalmology Retina.2024; 8(4): 399. CrossRef - Interpretable prediction model for assessing diabetes complication risks in Chinese sufferers
Ye Shiren, Ye Jiangnan, Ye Xinhua, Ni Xinye
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111560. CrossRef - Dose-response association of diabetic kidney disease with routine clinical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jianbo Guo, Chen Liu, Yifan Wang, Baoyi Shao, Tung Leong Fong, Ngai Chung Lau, Hui Zhang, Haidi Li, Jianan Wang, Xinyu Lu, Anqi Wang, Cheuk Lung Leung, Xin Wei Chia, Fei Li, Xiaoming Meng, Qingyong He, Haiyong Chen
eClinicalMedicine.2024; 69: 102482. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Computed Tomography Abdominal Fat and Skeletal Muscle Characteristics in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients With/Without Comorbid Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jinlei Fan, Liping Zuo, Mingyuan Hou, Bowen Wang, Yueming An, Baoli Hao, Dexin Yu
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(11): 2686. CrossRef - The concordance and discordance of diabetic kidney disease and retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study of 26,809 patients from 5 primary hospitals in China
Zhaoxiang Liu, Xianglan Li, Yanlei Wang, Yanxia Song, Qiang Liu, Junxia Gong, Wenshuang Fan, Chunmei Lv, Chenxiang Cao, Wenhui Zhao, Jianzhong Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ferroptosis: new insight into the mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy
Luxin Li, Yucen Dai, Dan Ke, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Dong Wei, Tongtong Wang, Yanjie Teng, Xiaohuan Yuan, Zhen Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting diabetic kidney disease for type 2 diabetes mellitus by machine learning in the real world: a multicenter retrospective study
Xiao zhu Liu, Minjie Duan, Hao dong Huang, Yang Zhang, Tian yu Xiang, Wu ceng Niu, Bei Zhou, Hao lin Wang, Ting ting Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xu Cao, Xiaomei Pei
Technology and Health Care.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Association between serum complements and kidney function in patients with diabetic kidney disease
Meng-chao Liu, Jia-lin Li, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Meng-di Wang, Xiang-gang Zhu, Yang-zi Chen, Yu-lin Wang, Wen-jing Zhao, Wen-quan Niu, Yao-xian Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coagulation Function and Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Real-World Observational Study
Meng-chao Liu, Wen-quan Niu, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Xiang-gang Zhu, Meng-di Wang, Jia-lin Li, Wen-jing Zhao, Yao-xian Wang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Punicalagin alleviates renal injury via the gut-kidney axis in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice
Qinglian Hua, Yaling Han, Haifeng Zhao, Haowen Zhang, Bei Yan, Shengjie Pei, Xin He, Yue Li, Xiangyuan Meng, Lei Chen, Feng Zhong, Duo Li
Food & Function.2022; 13(2): 867. CrossRef - Status and Trends of the Association Between Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetic Retinopathy From 2000 to 2021: Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Wenwen Lin, Yayong Luo, Fang Liu, Hangtian Li, Qian Wang, Zheyi Dong, Xiangmei Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Risk Threshold for Hemoglobin A1c Associated With Albuminuria: A Population-Based Study in China
Hong Lian, Hongshi Wu, Jie Ning, Diaozhu Lin, Chulin Huang, Feng Li, Ying Liang, Yiqin Qi, Meng Ren, Li Yan, Lili You, Mingtong Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change and microvascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Eun Sil Koh, Kyung Do Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(4): 932. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Dobesilate in Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Hao Zhang, Shao-Hua Guo, Zheng-Kai Xue, Ya-Ru Zhang, Jia-Rui Wang, Jing-Jin Che, Tong Liu, Hua-Yue Tao, Guang-Ping Li, Seung-Woon Rha, Swapnil-Zaman Ashraful-Haque, Kang-Yin Chen
Clinics.2021; 76: e2942. CrossRef - Elevated TG/HDL-C and non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratios predict mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients
Wenkai Xia, Xiajuan Yao, Yan Chen, Jie Lin, Volker Vielhauer, Hong Hu
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Perception Abnormalities Can Predict Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Wei-Ching Fang, Kuei-Mei Chou, Chiao-Yin Sun, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Yung-Chang Chen, Heng-Chih Pan
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2020; 45(6): 926. CrossRef - Association between nonalbumin proteinuria and renal tubular damage of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its clinical relevance in patients with type 2 diabetes without albuminuria
Eugene Han, Mi-Kyung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 255. CrossRef - Detection of Lower Albuminuria Levels and Early Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease Using an Artificial Intelligence-Based Rule Extraction Approach
Yoichi Hayashi
Diagnostics.2019; 9(4): 133. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of liraglutide on expression of CTGF and BMP‐7 in induced diabetic nephropathy
Maggie M. Ramzy, Ahlam M. Abdalla, Nagwa M. Zenhom, Ahmed M. Okasha, Aya E. Abdelkafy, Rabeh K. Saleh
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(10): 17512. CrossRef - Are blood lipids associated with microvascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients? A cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China
Hua Yang, Doris Young, Jian Gao, Yuanzhi Yuan, Minqian Shen, Yuan Zhang, Xueyan Duan, Shanzhu Zhu, Xiaoming Sun
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Discordance in risk factors for the progression of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ki‐Ho Song, Jee‐Sun Jeong, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Yu‐Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(3): 745. CrossRef - Risk factors for the development of micro-vascular complications of type 2 diabetes in a single-centre cohort of patients
Marsida Teliti, Giulia Cogni, Lucia Sacchi, Arianna Dagliati, Simone Marini, Valentina Tibollo, Pasquale De Cata, Riccardo Bellazzi, Luca Chiovato
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2018; 15(5): 424. CrossRef - Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 224. CrossRef - Determinants of the Risk of Diabetic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Retinopathy Independent of Glucose Exposure
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 444. CrossRef
- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
- A Case of Concurrent Emphysematous Pyelonephritis and Emphysematous Cholecystitis in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus.
- Se Hyung Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Jong Young Lee, Tae Hyuck Choi, Gil Hyun Gang, Myoung Sook Shim, Jin Yub Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(3):262-266. Published online May 1, 2005
- 1,200 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Several unusual infections such as malignant otitis externa, rhinocerebral mucormycosis, emphysematous pyelonephritis and emphysematous cholecystitis exclusively occur in diabetic patients. Each of these diseases is a rare, but potentially life-threatening infection. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and early medical and operative intervention will be necessary for these diseases. We report herein a very rare case in which emphysematous pyelonephritis and emphysematous cholecystitis were simultaneously diagnosed. A 45-year-old man, who was previously diagnosed with secondary diabetes mellitus due to chronic alcoholic pancreatitis ten years earlier, presented with fever and right upper quadrant abdominal pain for 3 days. Abdominal computed tomography showed an air-fluid level in the lumen of the gall bladder and there was gas collection within the right renal parenchyma. Broad-spectrum antibiotics therapy was initiated and cholecystectomy and right nephrectomy were performed. Escherichia coli bacteria were isolated from the culture of the blood, urine and sputum. The patient recovered and was discharged in a healthy state
- Hemichorea Associated with Type II Diabetes Mellitus.
- Ju Hee Maeng, Hee Sup Lee, Jin Gun Jang, Bae Gun Park, Kwang Deog Jo, Myoung Sook Shim, Jin Yub Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(4):362-366. Published online August 1, 2003
- 938 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hemichorea has been reported as a rare complication of nonketotic hyperglycemia. We report a diabetic patient who developed paroxysmal hemichorea. When hyperglycemia is corrected, the movement disorder resolves within a few days. The MR images showed high signal intensity on T1-weighted images and low signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the left basal ganglia contralateral to the involuntary movement. We present a case of hemichorea in a poorly controlled diabetic patient.
- Clustering of Risk Variables in Insulin Resistance Syndrome in Jungup District, Korea.
- Sang Wook Kim, Myung Hoe Huh, Young Il Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Moo Song Lee, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(6):843-856. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,074 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Insulin resistance syndrome (IRS), a clustering of hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance, low HDL cholesterol and high triglyceride, is prevalent in Korea. We studied the correlational structure of IRS using factor analysis to evaluate whether a single process underlies in the clustering of these risk factors. METHODS: Factor analysis was performed using data from 1,018 non-diabetic subjects (388 men and 630 women) who participated in the Jungup epidemiological study. RESULTS: Factor analysis reduced 9 correlated risk factors to 4 independent factors, each reflecting a different aspect of IRS: hypertension factor (increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure), glucose intolerance factor (increased fasting and postload glucose), obesity factor (increased body mass index, waist circumference, and increased insulin), and dyslipidemia factor (increased trigly- cerides and decreased HDL cholesterol). Increased insulin was also loaded into dyslipidemia factor in men and glucose intolerance factor in women. These factors explained about 70% of the total variance in the data. Three factors such as the glucose intolerance factor, the dyslipidemia factor and the obesity factor, were linked through mutual association with hyperinsulinemia, while hypertension factor was not associated with hyperin- sulinemia. Age-adjusted mean BP by BMI tertile and fasting insulin level tertile for men and women increased progressively with increase in BMI in men and women. There was no significant elevation of mean BP according to increase in fasting insulin level. In contrast to premenopausal women in whom hyperinsulinemia show mutual association with the glucose intolerance factor, the dyslipidemia factor, and the obesity factor, hyperinsulinemia was only loaded into obesity factor in postmenopausal women. CONCLUSION: These results suggested that more than one process underlies the clustering of IRS. In sulin resistance alone did not seem to be the single underlying mechanism of IRS. Especially, hypertension was not correlated with hyperin- sulinemia.
- Leptin Concentration in Diabetin and Non-diabetin Subjects in the Community Population.
- Kee Up Lee, Seong Kwan Hong, Sang Wook Kim, Young Il Kim, Yun Ey Chung, Moo Song Lee, Joong Yeoul Park, Jin Yup Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(4):592-600. Published online January 1, 2001
- 890 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It has been suggested that adipose tissue releases leptin, a satiety factor, which circulates in blood and acts on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite. However, serum leptin concentration in obese human subjects is higher than that in lean subjects, suggesting leptin resistance. Although there have been several studies investigating serum leptin concentrations in Korean subjects, there has been no population-based study. This study was undertaken to investigate serum leptin concentration and associated factors in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects living in a rural area of Korea. METHOD: Among 898 subjects originally included in the Jung-up epidemiologic study, 119 men and 124 women with varying degrees of glucose tolerance were randomly selected. Serum leptin concentration was measured by radioimmunoassay. RESULTS: In agreement with previous studies, women had significantly higher serum leptin concentration than men. Serum leptin concentration in Korean men and women was apparently lower than in other populations, even after adjustment for BMI. Leptin concentration was not different among the three groups of glucose tolerance (normal glucose tolerance, impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes). Serum leptin concentration was positively correlated with serum true insulin, proinsulin and BMI in non-diabetic subjects. Serum leptin concentration was also significantly related with serum proinsulin/true insulin ratio in non-diabetic women. CONCLUSION: Serum leptin concentration in Korean subjects was lower than that reported in other populations. Serum leptin concentration was associated with BMI, serum true insulin and proinsulin levels in non-diabetic subjects, but not in diabetic ubjects.
- Lack of Effectiveness of Glomerular Hyperfiltration on Development of Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: five Year Follow-up Study.
- Eun Sook Kim, Sang Wook Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(2):155-161. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,060 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glomerular hyperfiltration (GHF) is found in 30-40% of patients with type 1 diabetes at the onset of the disease. Several lines of evidence suggest that this might be responsible for the development of diabetic nephropathy. However, it is still controversial whether GHF is a risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes. This led us to perform a five-year-prospective study in normoalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 68 patients with type 2 diabetes were studied prospectively, They were all normoalbuminuric initially. Glomerular filtration rate was determined by the 51Cr-EDTA single injection method and urinary albumin excretion rate by the radioimtnunoassay method. RESULTS: GHF was present in 19 out of 68 patients. At follow-up, l7 out of 49 patients of the normofiltration group and 3 out of 19 patients of GHF group progressed to microalbuminuria (p>0.05). Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that the known duration of diabetes, systolic hypertension, and the presence of retinopathy were independently associated with the development of microalbuminuria. CONCLUSION: Our study suggests that GHF does not predict the subsequent development of diabetic nephropathy as indicated by the elevation of the urinary albumin excretion rate during the five year interval.
- Microalbuminuria in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Subjects: A population Based Study.
- Young Il Kim, Yun Ey Chung, Jin Yup Kim, Sang Wook Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Moo Song Lee, Joong Yeoul Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(1):79-86. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,143 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Microalbuminuria is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetic patients and non-diabetic subjects. This study was undertaken to determine the prevalence ot microalbuminuria among diabetic and non-diabetic subjects in Korea and to determine the factors associated with microalbuminuria. METHOD: A sample of 1,791 subjects aged > 40 years living in Jungup district were selected from the 28,380 inhabitants using a random cluster sampling method. Among these subjects, 1,006 of them (56.1%) underwent the 75 g oral glucose tolerance test that was also part of the timed overnight urine collection. 46 subjects were excluded because they had signs of urinary tract infection (n=41) or overt proteinuria (n=5). Microalbuminuria was defined as urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) between 20 and 200 pg/min. RESULTS: Subjects with microalbuminuria had a higher weight and body mass index (BMI), abdominal circumference, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP), fasting and 2hr plasma glucose, fasting semm insulin and proinsulin concentrations than subjects without microalbuminuria. The prevalence of micro- albuminuria increased as the glucose tolerance worsened[6.0% in normal glucose tolerance, 11.8% in impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and 21.8% in diabetes, respectively; x trend=25.9, p<0.(0001]. Mean UAER of subjects with hypertension was greater than that of subjects without hypertension (7.8+0.9ug/min vs. 9.6+0.7ug/min, p<0.001). Univariate analysis revealed that the UAER was significantly (p<0.05) correlated with weight and BMI, abdominal circumference, systolic and diastolic BP, fasting and 2hr plasma glucose, fasting serum insulin and proinsulin after sex-adjustment. Multiple regression analysis revealed that weight or BMI, diastolic BP, 2hr plasma glucose and fasting serum insulin were independently associated with UAER in non-diabetic subjects. CONCLUSION: The present study demonstrates that the prevalence of microalburninuria is higher in patients with glucose intolerance. The association of the UAER with BMI, diastolic BP, 2hr plasma glucose and fasting serum insulin suggest that microalbuminuria is a feature of the insulin resistance syndrome.
- Prevalence of Insulin Resistance Syndrome in Subjects Living in Jungup District , Korea.
- Sang Wook Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Young Il Kim, Moo Song Lee, Hyeong Ho Kim, Joong Yeoul Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(1):70-78. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,045 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The clustering of hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance, low HDL cholesteml and high triglyceride is known as insulin resistance syndrome (IRS). We studied the prevalence of insulin resistance syndrome among subjects living in Jungup district, Korea. METHODS: Among a total of 151,000 subjects over 40 years of years living in Jungup district, a sample of 1,791 was selected using a random cluster sampling method. Oral glucose tolerance test revealed 1,018 subjects with normal or impaired glucose tolerance. The IRS was defined as the coexistence of two or more components of triad; hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia (triglycerides >= 200mg/dL and HDL <45 mg/dL for woman, HDL < 35 mg/dL for men). RESULTS: Twenty-one percent of men and 45% of women were obese and 50.8% and 61.9% were hypertensive. Eleven percent of men and 16 percent of women were found to have dyslipidemia. The prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance was 10.2% for men and 15.7% for women. The prevalence of IRS in the Jungup population was 12.8% for men and 19.6% for women. The prevalence of IRS increased according to the plasma level of insulin. There was a positive correlation between the number of components of IRS and the level of fasting plasma insulin. CONCLUSION: We conclude that the prevalence of IRS is high in Korean subjects. The close correlation between the IRS components and fasting insulin level suggests that cardiovascular risk is associated with insulin resistance.
- Effect of Decreased Plasma Free Fatty Acids by an Antilipolytic Agent on Plasma Glucose Level and Liver Glycogen Content in Streptozotocin - induced Diabetic Rat.
- Yun Ey Chung, Sang Wook Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(1):46-54. Published online January 1, 2001
- 936 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Increased availability of plasma free fatty acid (FFA) leads to an inhibition of glucose utilization in peripheral tissue and to an increase of gluconeogenesis in the liver. A previous study has shown that a decrease in plasma FFA profoundly inhitbits hepatic gluconeogenesis, but total hepatic glucose production is maintained due to a com pensatory increase in glycogenolysis. It has been suggested that this hepatic autoregulatory mechanism is defective in the diabetic state, but there has been no firm evidence to confirm this. This study was performed to see the effect of decreasing plasma FFA on plasma glucose and hepatic glucose metabolism in diabetic rats, METHODS: Eight nondiabetic and 8 streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats were used. Blood sampling for plasma glucose and free fatty acid and liver biopsy for measurement of glycogen content were done after intravenous phenobarbital ancsthesia. Acipimox (50 mg/kg in saline) was administered via gastric tube. Plasma glucose and FFA were measured at 30, 60 and 120 min. Liver biopsy was repeated at 120 min. RESULTS: Baseline plasma glucose and FFA were higher in diabetic rats than in nondiabetic rats (18.8 +1.4 mmol/L vs. 6.9+0.8 mmol/L, 720+/-36 umol/L vs. 420+40 umol/L p<0.001 respectively). Hepatic glycogen content was higer in nondiabetic rats (31.8 +1.6mg/g liver vs. 26.02.Dmg/g liver, p<0.01). After acipimox administration, plasma glucose decreased profoundly in diabetic rats (18.8+1.4 mmol/L to 9.2+1.2 mmol/L, p<0.001) but not in nondiabetic rats. Glycogen content was significantly reduced in both groups (p<0.001). However, the difference in the contents was much smaller in the diabetic group compared with the nondiabetic group (6.5+2.1 mg/g liver vs. 19.2+ l.9 mg/g liver, p<0.001). CONCLUSION: 1t is suggested that the intrahepatic autoregulatory mechanism, which maintains hepatic glucose production constant in nondiabetic rats, is defective in diabetic rats.
- The Effects of Metformin Given into the Brain on Food Intake and a Expressions of Hypothalamic Neurotransmitters in the Rats.
- Eun Sook Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Sang Wook Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Ki Up Lee, Sung Kwan Hong
- Korean Diabetes J. 1998;22(4):475-481. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,016 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metformin, a biguanide agent, is an oral hypoglycemic agent frequently prescribed to non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. In adclition to the glucose lowering effect, it is known to suppress fol intake, but the action mechanism for food intake suppression is not known yet. Hypothalamic neuropeptide Y (NPY) is recently identified that strongly stimulates food intake and melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) is also known to be involved in the ingestion of foods. The effects of mettormin on these substances are not known yet. We tried to define the effect of metformin administered into the lateral ventricle on the amount of food intake and mRNA expressions of NPY and MCH. METHODS: Each rat was housed in a separate cage, and brain cannula was set into the lateral ventricle and proper position was checked by the response to angiotensin-II injection. Metformin l ug (1 ug/uL) or normal saline (1 uL) were injected daily into the lateral ventricle for 4 days in the Metformin group (n=7) and Control group (n=6) respectively, and the amount of food intake and weight change were recrded. Expressions of corticotropin releasing hormone mRNA in paraventricular nucleus, NPY mRNA in arcuate nucleus, and MCH mRNA in lateral hypothalamus were measured by the in situ hybridization technique. RESULTS: The amount of food intake was lower in metformin group than that in control group by 14~35% during the study period (p<0.05). Changes of body weight was -18+9 g (mean+SD) in metformin group and -2+11 g in control group. But mRNA expressions of NPY, MCH and CRH were not different between the groups (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Metformin injected into the brain reduced the amount of food intake and body weight without the changes of NPY and MCH mRNAs. This study suggests that metformin suppress food intake by directly acting in the brain, but these effects are not through the changes of NPY and MCH mRNA expressions.
- High Serum Lipoprotein ( a ) Levels in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy.
- Hyung Joo Park, Chul Hee Kim, Yun Ey Chung, Sang Wook Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1998;22(3):338-343. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,084 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To examine the possible association between serum lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) concentration and proliferative diabetic retinopathy(PDR) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: A total of 412 Korean outpatients with type 2 diabetes were examined. Diabetic retinopathy was determined by fundoscopic examination by an ophthalmologist and/or by fluorecein angiography. Semm Lp(a) levels were measured by one step sandwich ELISA method. RESULTS: The patient with PDR had higher serum Lp(a) levels than those with no retinopathy or non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy(NPDR). Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that serum Lp(a) level and the presence of diabetic nephropathy were independent variables having a statistically significant association with PDR. CONCLUSION: Korean type 2 diabetic patients with PDR had higher serum Lp(a) levels compared with those with no retinopathy or NPDR. Although these results suggested that Lp(a) might play a role in the occlusion of retinal capillaries leading to PDR, further prospective studies are required to prove causal relationship.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





